The Corrosion Challenge in Chemical Processing
Chemical processing facilities utilize stainless steel equipment for a wide range of applications, from storage tanks and piping systems to reactors and valves. Stainless steel is prized for its natural resistance to corrosion, but in environments where it is exposed to potent acids, alkalis, solvents, and chlorine compounds, even stainless steel can deteriorate over time.
Corrosion in these settings is particularly insidious because it can occur beneath the surface, weakening the integrity of equipment without showing immediate signs of damage. If left unchecked, corrosion can lead to leaks, contamination of products, or complete equipment failure, which can result in significant downtime, expensive repairs, or worse—catastrophic accidents.
How Passivation Protects Stainless Steel
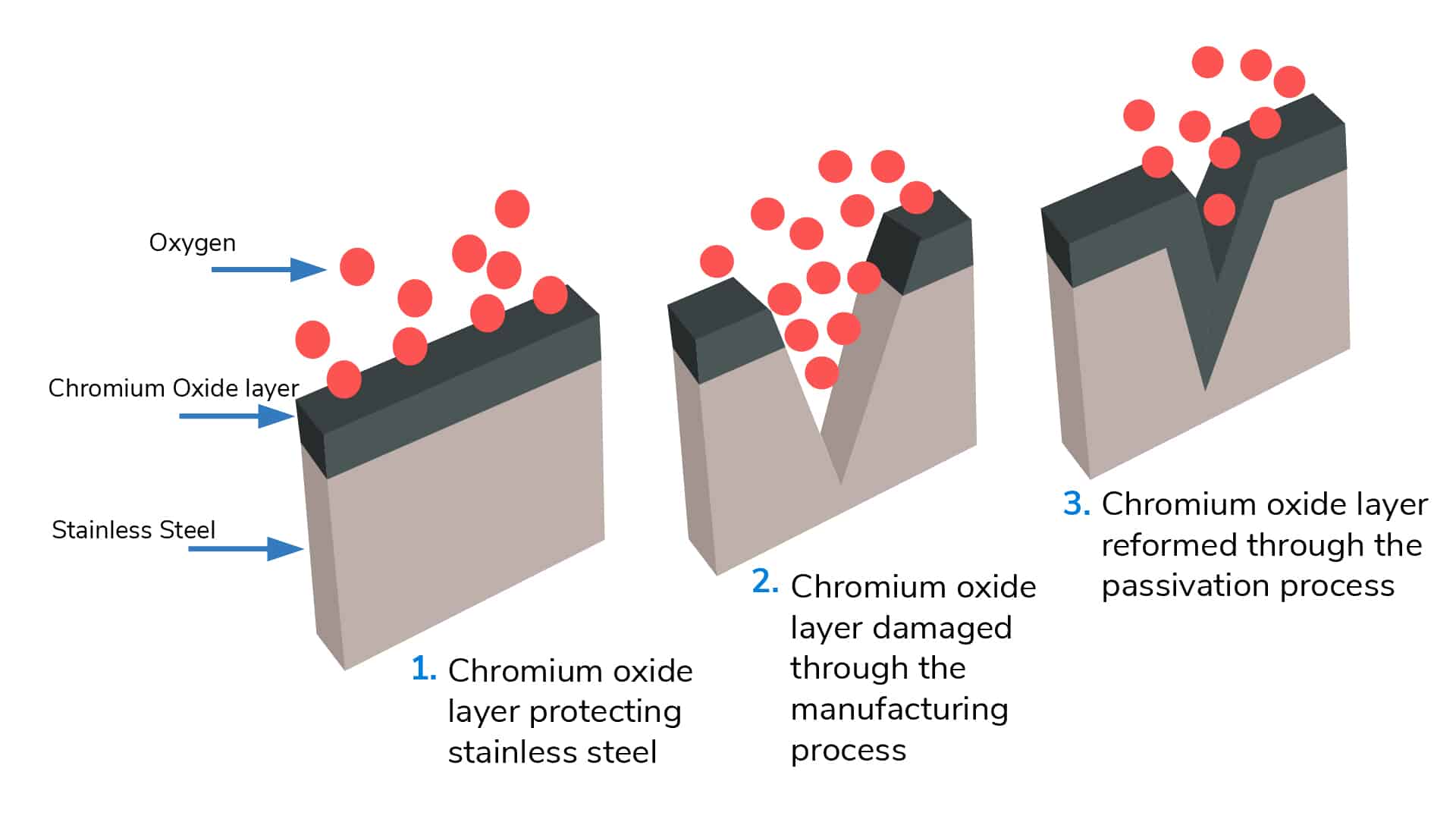
What is passivation? Passivation is a chemical process that enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by removing surface contaminants and promoting the formation of a protective oxide layer. When stainless steel is exposed to harsh environments, microscopic particles of iron and other impurities can embed themselves in the material’s surface. These contaminants can act as initiation points for corrosion, especially when exposed to the highly reactive chemicals found in chemical processing plants.
During passivation, the stainless steel components are treated with a nitric or citric acid solution that dissolves these impurities, leaving behind a clean and contaminant-free surface. This process encourages the formation of a passive oxide layer on the surface of the steel, which acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying metal from corrosive elements.
Benefits of Passivation for Chemical Processing Equipment
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
- The primary benefit of the passivation of stainless steel in the chemical processing industry is the significant improvement in corrosion resistance. By removing contaminants and fostering a strong passive oxide layer, passivated stainless steel can endure prolonged exposure to aggressive chemicals, acids, and gases without succumbing to corrosion. This added layer of protection helps extend the lifespan of critical equipment.
- Improved Safety and Reliability
- Corrosion can compromise the safety and reliability of chemical processing equipment, leading to leaks or failures that can pose significant risks to workers and the surrounding environment. Passivation helps prevent these risks by ensuring that stainless steel components remain intact and free from corrosion-related damage. Equipment that undergoes regular passivation is less likely to fail, promoting a safer working environment and reducing the potential for costly incidents.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs
- Chemical processing facilities are complex operations with a vast array of stainless steel equipment, much of which requires regular maintenance. Passivation reduces the need for frequent repairs by protecting equipment from corrosion, allowing facilities to operate more efficiently. The extended lifespan of passivated stainless steel means that equipment can function longer without requiring replacement or extensive maintenance, leading to significant cost savings over time.
- Compliance with Industry Standards
- The chemical processing industry is heavily regulated, with strict standards for equipment performance, safety, and reliability. Passivation helps facilities meet these standards by ensuring that their stainless steel components are free from corrosion and contamination. Passivated equipment performs better and maintains compliance with industry guidelines, ensuring smooth operations and reducing the risk of regulatory issues.
Applications of Passivated Stainless Steel in Chemical Processing
Passivation plays a vital role in a wide range of applications within the chemical processing industry. Some key uses of passivated stainless steel include:
- Storage Tanks and Pressure Vessels: Large tanks that store corrosive liquids and gases benefit from passivation, as it prevents corrosion and preserves the structural integrity of the tanks over time.
- Piping Systems: Passivation ensures that stainless steel pipes resist corrosion, particularly in areas exposed to acids or high-moisture environments, reducing the risk of leaks and contamination.
- Reactors and Mixing Vessels: These components are often exposed to aggressive chemicals during manufacturing processes. Passivation provides an added layer of protection, improving the reliability and performance of these critical systems.
- Valves and Fittings: Small yet crucial components like valves and fittings must maintain their corrosion resistance to ensure the smooth operation of chemical processing systems. Passivation helps these parts withstand harsh chemical exposure and maintain functionality.
Conclusion
In the chemical processing industry, where stainless steel components are exposed to some of the most corrosive environments imaginable, passivation is an indispensable step in protecting equipment from premature failure. By removing surface contaminants and enhancing corrosion resistance, passivation ensures that stainless steel parts perform reliably under extreme conditions, promoting safety, reducing maintenance costs, and extending the life of critical equipment.
For chemical processing facilities looking to safeguard their operations, investing in passivation is not just a preventative measure—it’s an essential process for ensuring long-term success.