Citric Acid Passivation
Citric Acid Passivation is the removal of contaminants or “free irons” from the surface layer of metals such to allow the growth of a natural, inert, oxide layer on the metal that restores its natural corrosion resistance by immersing parts in a bath of Citric Acid to make the metal “passive”. The passivation of Stainless Steel can be accomplished by other means, including Electropolishing and Nitric Acid Passivation. Citric Acid Passivation offers an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods while providing excellent results.
What is Citric Acid Passivation?
Understanding Passivation
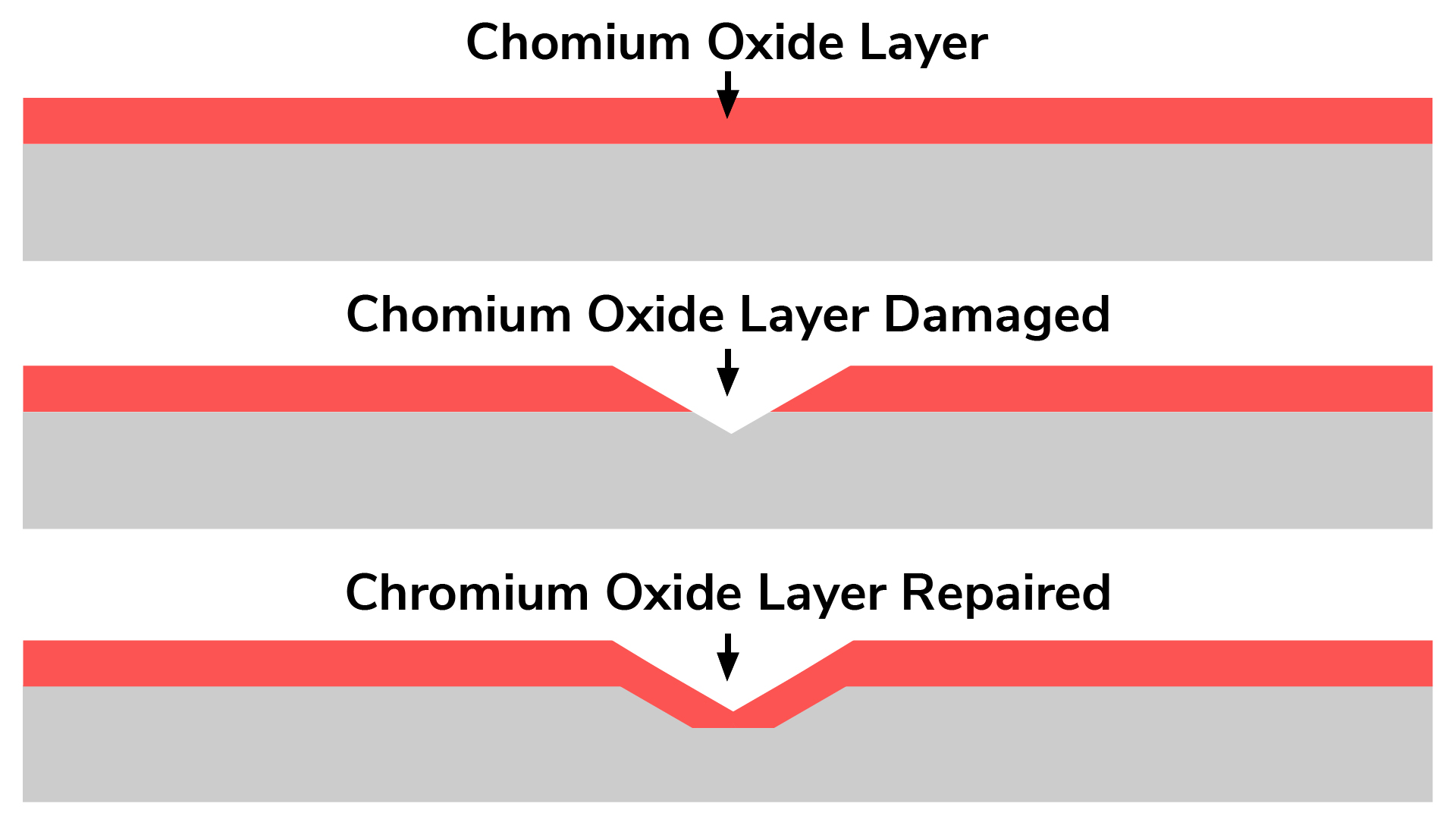
Contaminants left behind from the manufacturing process inhibit the formation of the oxide layer that forms on the outside layer of metals and protects metals like stainless steel from corrosion. Although stainless steel is inherently passive, these impurities left behind combine with the metal resulting in a corrosive reaction.
Manufacturers in industries that require a high level of cleanliness such as medical, aerospace, laboratory, and food manufacturing often rely on chemical passivation to improve performance, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Why Citric Acid Passivation
Citric Acid Passivation has become more widely accepted by industries such as Medical and Aerospace in recent years. It offers an effective alternative to nitric acid passivation with less handling concerns and is considered environmentally friendly being on the GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) list for the FDA making it ideal for both the medical and food manufacturing industries.
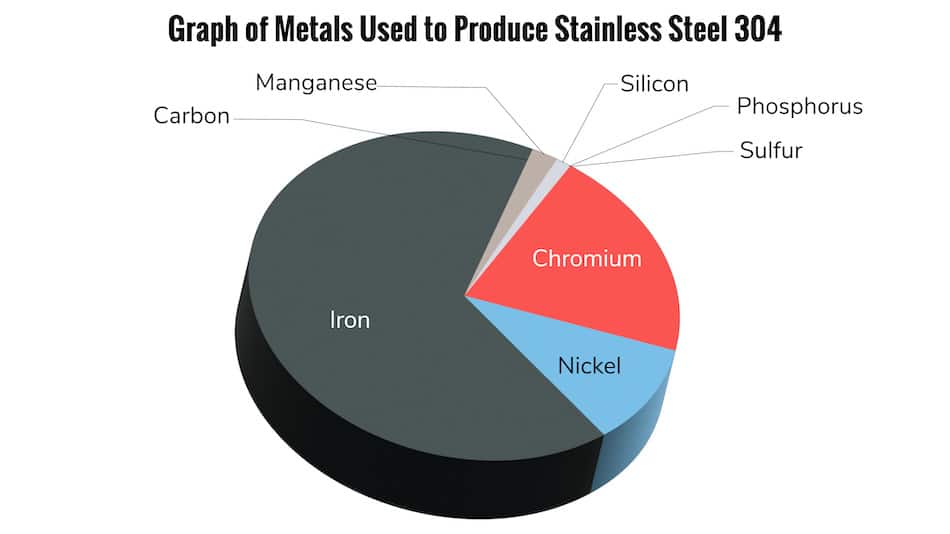
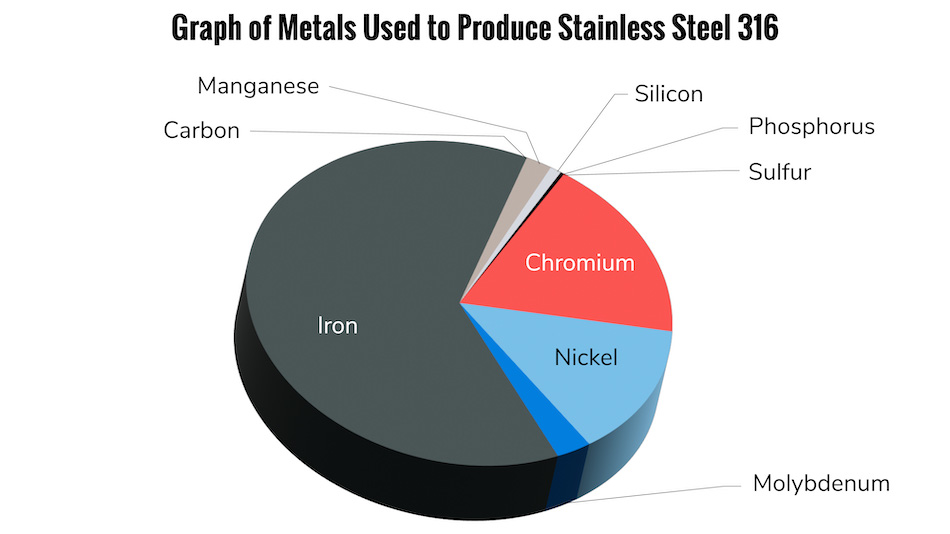
Additionally, citric solutions can effectively passivate a wider range of stainless-steel alloys compared to traditional nitric acid methods such as ASTM A967, Nitric 2.
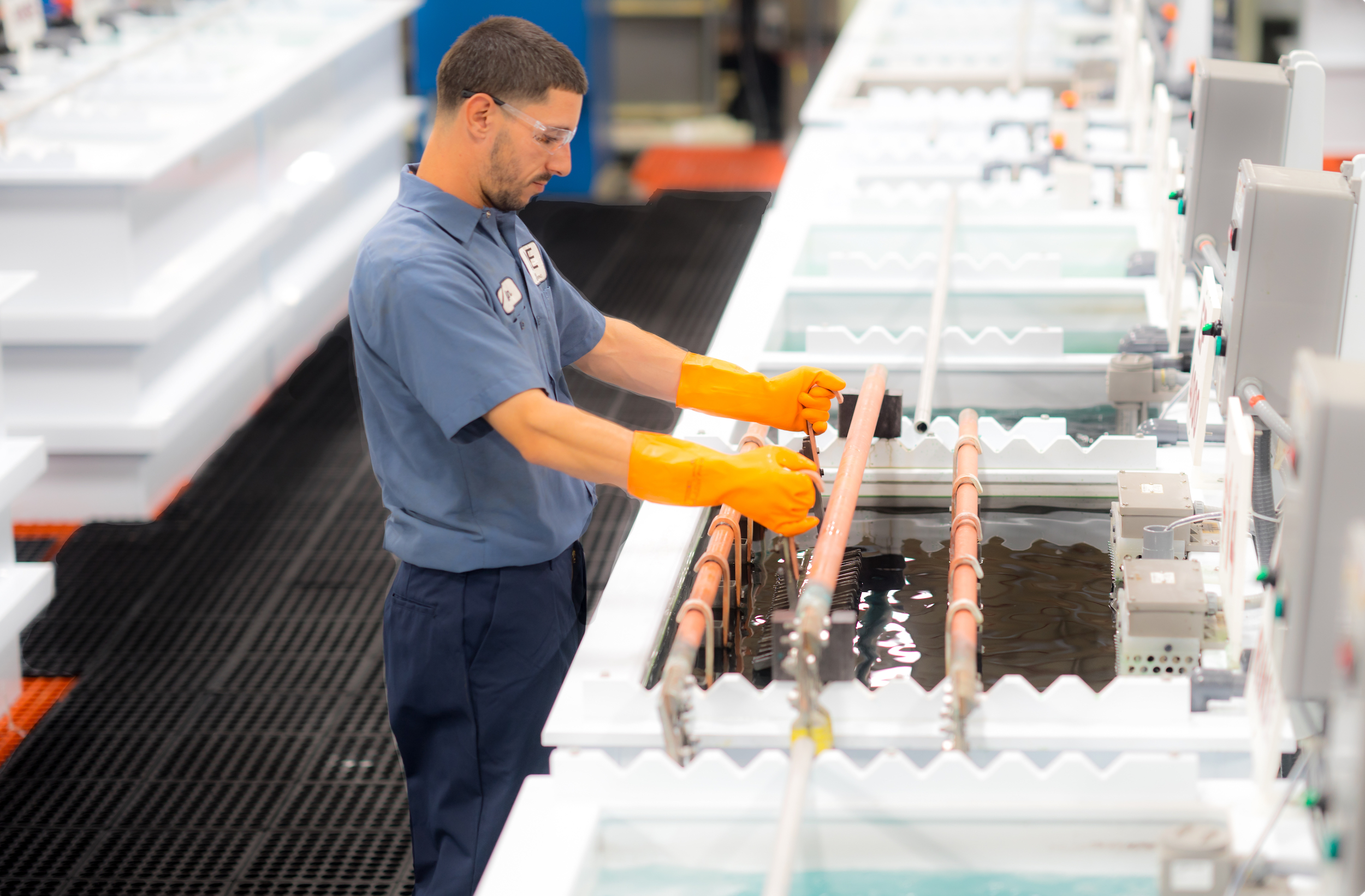
The Citric Acid Passivation Process
Step 1: Pre-Cleaning: Prior to the passivation process, stainless steel parts are subjected to an extensive pre-cleaning cycle to remove oils, grease, and metallic residues. The degreasing and cleaning of stainless-steel parts can be accomplished by a variety of commonly accepted methods, including acid pickle and an alkaline soak followed by a water rinse.
Step 2: Immersion Bath: After the removal of the organic and metallic residues from the surface of the part, they are then placed into a Citric Acid Passivation bath, specifically calibrated to meet ASTM A967 Citric 3 finishing standards. The three primary variables of Citric Acid Passivation to meet ASTM parameters are time, temperature, and concentration of acid.
Step 3: Final Cleaning & Dry: After the Citric Acid Passivation, parts are put through an extensive rinsing process concluding with a two-stage deionized rinsing process.
Step 4: Quality Testing & Inspection: Sample parts are tested to ensure they meet customer qualifications before being packaged for shipping.
Citric Acid Passivation Industry Standards
Most manufacturers’ standards meet two primary industry standards for citric acid passivation as set forth by ASTM International. ASTM International is a widely recognized and reputable standards organization charged with developing and publishing voluntary consensus technical data and standards for use in a wide range of materials and products. ASTM has two widely accepted standards, ASTM A967 and AMS 2700. New England Electropolishing’s processes adhere to the ASTM A967 Citric 3 standard.
The Passivation of Stainless Steel with Citric Acid
Discover the advanced technique of passivating stainless steel with citric acid, a method gaining popularity for its effectiveness in enhancing the corrosion resistance and surface quality of stainless steel components.
Citric acid passivation is a modern and eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods such as nitric acid passivation. It involves the use of citric acid solutions to remove free iron and other contaminants from the surface of stainless steel. This process promotes the formation of a passive oxide layer, significantly improving the steel’s resistance to corrosion.
Safety: Citric acid presents fewer safety hazards compared to other passivation methods, making it a preferred choice for many industries.
Compliance: It meets stringent regulatory requirements and industry standards while delivering outstanding results in surface treatment.
Partnering with Experts in Citric Acid Passivation
At New England Electropolishing, we specialize in the application of citric acid passivation techniques, ensuring your stainless steel components meet the highest standards of durability and quality. Our expertise and commitment to excellence guarantee optimal performance and reliability in every application.
If you have any further questions about Citric Acid Passivation or stainless steel passivation through electropolishing and whether it is right for your stainless-steel passivation needs, please contact us today and we would be happy to speak with you.
To learn more about how Electropolishing can passivate, improve surface finish, and enhance the aesthetics of stainless steel, please click here.
The Passivation of Stainless Steel with Citric Acid
Contact us for Your Citric Acid Passivation Needs
Contact us today to see if citric acid passivation is the right method for your passivation needs. We are happy to provide a free estimate and even a free sample part passivated and shipped back to you at no cost.
Electropolishing Resources

What is Electropolishing?
Electropolishing is an electrochemical and reverse plating process that removes the outer layer of skin on a metal...

The Electropolishing Process
The electropolishing process is initiated by immersing a metal part into a temperature-controlled bath of electrolyte...

Benefits of Electropolishing
Curious about the benefits of putting your parts through the electropolishing process? Read along below where we...

How Much Material Does Electropolishing Remove?
Electropolishing, when done properly is a highly controllable process which removes as little as...

How Much Will Electropolishing Improve the Surface Finish of My Part?
Ra and RMS are both representations of surface roughness. Ra is calculated as the roughness average of a surface’s...

Electropolishing Frequently Asked Questions
Learn the difference between electropolishing and electroplating as well as how the electropolishing process works...

What is ASTM B912?
ASTM B912 is an industry standard for the passivation of stainless steel alloys through electropolishing...

What is ASTM A967?
ASTM A967 is an industry standard specification for the chemical passivation treatments for stainless...

What is ISO 13485?
ISO 13485 is a standard that applies specifically to medical devices. ISO 13485 is designed to be...
