How much material does electropolishing remove?
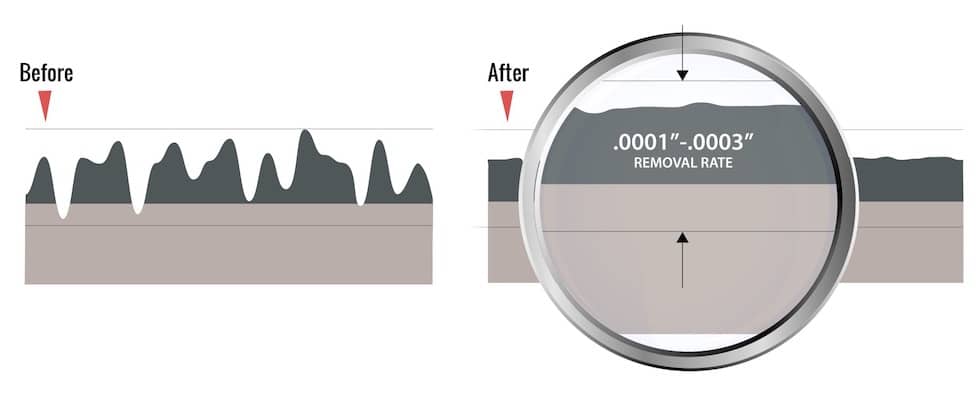
Electropolishing can remove as little as .0001” per surface or .0002” total material. Material removal can be increased by adding more time and/or direct current to the process. Electropolishing will typically remove between .0002” to .0003” per surface depending on a part’s size and square footage.
How Much Material Does Electropolishing Remove?
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process used to smooth and polish the surface of stainless steel tools and components. It is a great way to improve achieve stainless steel passivation and improve the aesthetic appeal of stainless steel parts, but how much material does electropolishing actually remove? In this article, we will discuss the effects of electropolishing on the thickness of stainless steel products.
Electropolishing stainless steel, when done properly is a highly controllable process, which removes as little as .0001” per surface or .0002” total material. Material removal can be increased by adding more time and/or direct current to the process. Electropolishing will typically remove between .0002” to .0003” per surface depending on a part’s size and square footage.
Variables that affect electropolishing removal rates
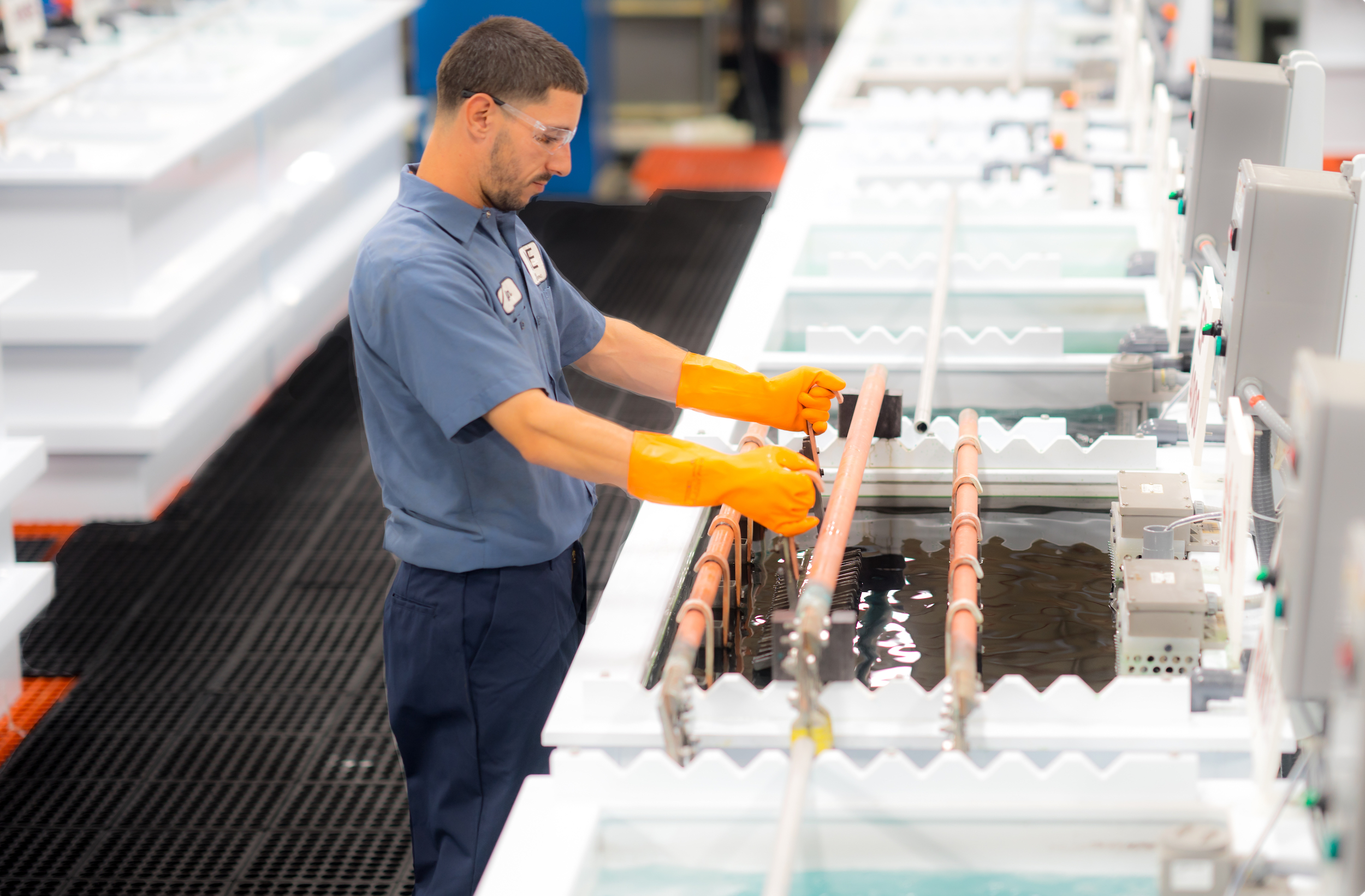
There are many variables involved in the Electropolishing process such as time, amperage, bath temperature, bath chemistry, and specific gravity. New England Electropolishing has tightly controlled processes for thousands of parts that yield consistent repeatable results on each order. The electropolishing process works by removing thin layers of material and free iron from the surface of a stainless steel part in order to achieve passivation and a smooth finish that is easier to clean and resistant to corrosion. This is done by immersing the part in an electrolyte solution and applying an electrical current to it. The current causes ions from the solution to be deposited onto the surface of the part, which then reacts with any impurities or contaminants on its surface. This reaction removes small amounts of material from the part.
Removal rates are generally very consistent assuming parts have the same starting thickness. Edges and radius generally have slightly more material removal as they are higher current areas. This is often a plus as burrs and high points will be brought down and removed. Additionally, the surface roughness of parts (Ra, RMS) will be reduced as more material is removed. On average, the surface roughness of parts can be reduced between 25-35% assuming a moderate amount of material removal.
Many of the parts we electropolish for the medical industry have strict tolerances. These are often critical components of a device where form, fit and function are essential. In these instances, NEE will measure parts before and during processing to ensure product consistency. Records are kept with each job order. Additionally, we can share removal data with our customers to maintain transparency and confirm results. NEE often develops electropolishing processes for customers through product sampling. We often will provide customers with multiple groups of samples with different removal rates. Once we receive positive feedback, the electropolishing process will be locked in our ERP system for future orders.
There are several benefits of electropolishing stainless steel parts; however, it is important to understand how much material will be removed during each cycle. Generally speaking, electropolishing can remove up to .0001” per surface or .0002” total material per cycle from stainless steel surfaces; however this amount varies depending on several factors, so it’s best to consult with an experienced stainless steel electropolishing company before proceeding with electropolishing for your specific needs.
Please consider New England Electropolishing for your next application. NEE is ISO 9001, ISO 13485 accredited and adhere to ASTM B912, and ASTM A967 standards for the passivation and electropolishing of stainless steel. In addition, NEE has developed a proprietary tool that serves as a comprehensive solution for quality control and customer collaboration, learn more about our Inspection Manager Tool. Our organization looks forward to developing an electropolishing process with your team!
Understanding RA & RMS
“RMS and RA are two of the most widely used tools for measuring metal surface roughness. RMS stands for Root Mean Square and is used to measure the surface roughness of irregular surfaces. Both RMS and RA are effective tools to measure the efficacy and results of stainless steel electropolishing.”
Electropolishing Resources

What is Electropolishing?
Electropolishing is an electrochemical and reverse plating process that removes the outer layer of skin on a metal...

The Electropolishing Process
The electropolishing process is initiated by immersing a metal part into a temperature-controlled bath of electrolyte...

Benefits of Electropolishing
Curious about the benefits of putting your parts through the electropolishing process? Read along below where we...

How Much Material Does Electropolishing Remove?
Electropolishing, when done properly is a highly controllable process which removes as little as...

How Much Will Electropolishing Improve the Surface Finish of My Part?
Ra and RMS are both representations of surface roughness. Ra is calculated as the roughness average of a surface’s...

Electropolishing Frequently Asked Questions
Learn the difference between electropolishing and electroplating as well as how the electropolishing process works...

What is ASTM B912?
ASTM B912 is an industry standard for the passivation of stainless steel alloys through electropolishing...

What is ASTM A967?
ASTM A967 is an industry standard specification for the chemical passivation treatments for stainless...

What is ISO 13485?
ISO 13485 is a standard that applies specifically to medical devices. ISO 13485 is designed to be...
