Passivation Services: Nitric & Citric Options
Enhancing Corrosion Resistance for Critical Stainless Steel Components
Passivation is a chemical treatment process used to improve the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by removing free iron and surface contaminants that can compromise its natural protective layer. At New England Electropolishing, we offer both nitric and citric acid passivation options to meet the exacting demands of industries such as medical device manufacturing, aerospace, semiconductor, and food processing.
Comparing Two Proven Approaches to Stainless Steel Passivation
Each method is effective in promoting the formation of a durable chromium oxide layer on the surface of stainless steel, but they differ in their chemical composition, environmental impact, and regulatory requirements. Our team will help you determine the right process for your material, application, and industry standards.
Nitric Acid Passivation
Industry-Standard Performance for Stainless Steel Alloys
Nitric acid passivation is a widely accepted method for enhancing the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. The process uses nitric acid—sometimes with added oxidizers—to dissolve free iron from the surface without affecting the integrity of the metal. As a result, the chromium present in the stainless steel reacts with oxygen to form a stable, passive oxide layer that protects against future corrosion.
Key Benefits:
-
Proven and widely accepted across aerospace, defense, and industrial applications
-
Compatible with a wide range of stainless steel grades
-
Backed by specifications like ASTM A967, AMS 2700, and others
-
Strong oxidizing power ensures complete contaminant removal
Considerations:
-
Involves hazardous chemicals that require careful handling and disposal
-
Regulatory and environmental restrictions may apply in certain industries or regions
Citric Acid Passivation
A Safer, Environmentally Responsible Alternative
Citric acid passivation offers a modern, eco-conscious alternative to nitric acid, achieving similar levels of corrosion protection without the safety and environmental risks associated with stronger acids. The citric acid solution binds to free iron and removes other contaminants, allowing the chromium oxide layer to naturally regenerate through the passivation process.
Key Benefits:
-
Non-toxic, biodegradable, and safer for personnel and the environment
-
Effective on a broad range of stainless steel alloys, including welded and machined parts
-
No toxic fumes, making it ideal for cleanroom or medical manufacturing settings
-
Reduced regulatory and waste disposal concerns compared to nitric-based methods
Considerations:
-
Requires controlled process parameters (temperature, concentration, and dwell time)
-
May require additional validation testing in some industries
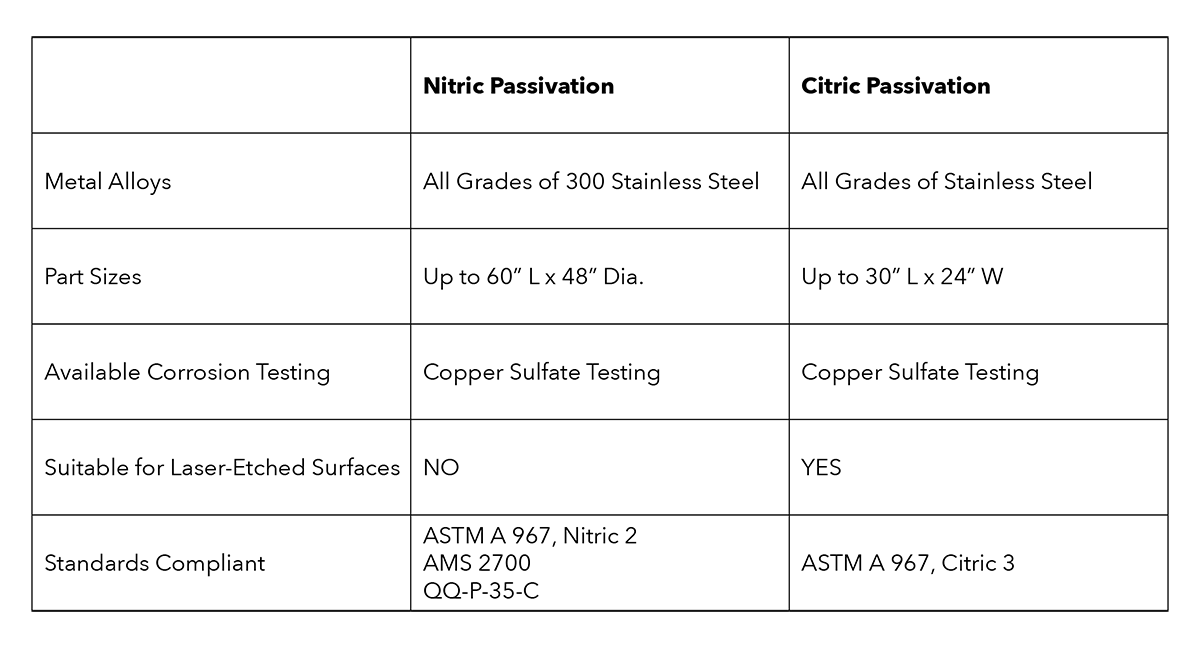
Nitric vs. Citric Acid Passivation: A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | Nitric Acid Passivation | Citric Acid Passivation |
|---|---|---|
| Chemistry | Nitric acid (HNO₃), sometimes with oxidizing agents | Citric acid (C₆H₈O₇), a weak organic acid |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective at removing free iron and oxides | Equally effective when properly controlled |
| Environmental Impact | Hazardous, requires strict handling and disposal | Biodegradable, non-toxic, environmentally friendly |
| Worker Safety | Requires ventilation and PPE for fumes and handling | Safer to handle with reduced health risks |
| Regulatory Restrictions | Heavily regulated in many regions | Fewer restrictions, easier to permit and manage |
| Compatibility | Broad compatibility with stainless alloys | Broad compatibility, including welds and complex parts |
| Cleanroom Suitability | May not be ideal due to fumes or residue | Preferred for medical and cleanroom applications |
| Waste Disposal Requirements | Requires hazardous waste management | Easier, more cost-effective disposal |
| Process Control Sensitivity | More forgiving with concentration/temperature | Requires tighter control of parameters |
| Industry Standards | Backed by ASTM A967, AMS 2700, etc. | Also compliant with ASTM A967 and validated testing |
Our Approach to Passivation
Whether your project calls for nitric or citric passivation, New England Electropolishing provides precision-controlled processes that meet stringent quality standards, including ASTM, AMS, and ISO specifications. We evaluate each job based on material type, end-use application, and performance requirements to deliver consistent, validated results every time.
Looking for guidance on the right passivation method for your component or industry?
Contact our team to learn more or request a quote.
"Passivation is a science and an art. By combining both, we meet your exact finishing requirements, whether you need one part of 100,000. Our customers tell us no one does stainless steel electropolishing better."
Imad JaberOperations Manager