What is passivation?
Passivation is a critical surface treatment used to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel and other corrosion-resistant alloys. The process works by removing contaminants—particularly free iron—from the surface and facilitating the formation of a thin, stable oxide layer. This invisible “passive film” acts as a protective barrier, shielding the metal from moisture, air, and other environmental elements that can cause corrosion.
Understanding Passivation
Passivation is a chemical process designed to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. While stainless steel is naturally resistant to rust and corrosion, its surface can still contain contaminants or impurities from manufacturing processes, handling, or exposure to elements. These contaminants can compromise its corrosion-resistant properties.
Passivation involves the removal of these impurities from the surface of stainless steel, typically through electropolishing or other chemical treatments such as citric acid passivation. This process effectively cleanses the material, allowing the re-formation of a protective chromium oxide layer. This oxide layer, known as the passive film, acts as a shield, fortifying the stainless steel against corrosion, oxidation, and other forms of degradation.
The Benefits of Passivation
Improved Corrosion Resistance
A properly passivated part is significantly more resistant to rust, pitting, and other forms of corrosion.
Longer Part Lifespan
By protecting the surface, passivation extends the functional life of stainless steel components—reducing failure rates and maintenance costs.
Preserved Material Integrity
The treatment is non-destructive, meaning it protects the material without compromising mechanical properties or dimensional tolerances.
Common Passivation Methods
While electropolishing has been scientifically proven to be the most effective means of achieving stainless steel passivation, several different processes are commonly used, each tailored to specific needs and environments. Here are the primary types:
Nitric Acid Passivation: The most common method, involving immersion in nitric acid to remove free iron and contaminants, promoting the formation of a protective chromium oxide layer.
Citric Acid Passivation: An environmentally friendly alternative to nitric acid, using citric acid solutions to achieve similar results without the use of strong oxidizing agents.
Electropolishing: A more advanced technique where the stainless steel is placed in an electrolytic bath, and an electric current is applied to remove surface material, enhancing passivation and surface smoothness.
Alkaline Cleaning: Used before acid treatment, this process involves cleaning the stainless steel with alkaline solutions to remove organic contaminants, oils, and greases but will not passivate the alloy.
How Passivation Works
1. Surface Cleaning
The process begins with thorough cleaning of the metal part to remove machining oils, debris, and heat-affected surface contaminants. This step is essential to prepare the surface for effective oxide layer formation.
2. Chemical Treatment
The clean part is then exposed to an acid solution—typically a citric acid or nitric acid bath. This treatment dissolves free iron and other embedded impurities without affecting the stainless steel matrix.
3. Oxide Layer Formation
Once contaminants are removed, a uniform, passive oxide film naturally forms on the surface. This layer is chemically inert, self-repairing, and resistant to further oxidation or corrosion.
The Chemical Composition of Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium, and often nickel, along with other elements depending on the grade. The typical chemical composition includes: Iron (Fe), Chromium (Cr), Nickel (Ni), Carbon (C), Manganese (Mn), Molybdenum (Mo), Silicon (Si), Phosphorus (P), and Sulfur (S).
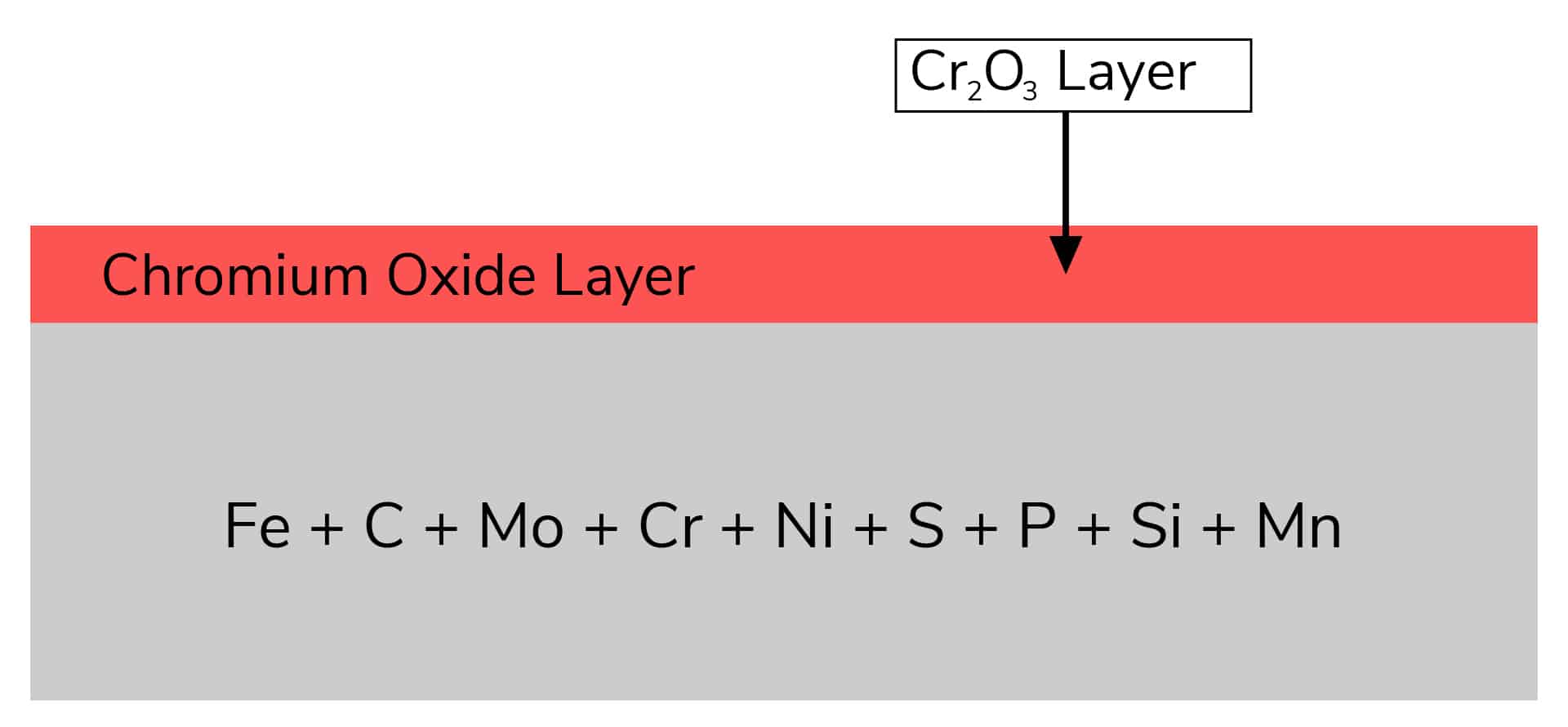
The Formation of the Chromium Oxide Layer on Stainless Steel
The formation of the chromium oxide layer on stainless steel is a critical process that gives the material its corrosion-resistant properties. When stainless steel is exposed to oxygen, chromium within the alloy reacts with the oxygen from the environment to form a thin, stable layer of chromium oxide (Cr2O3) on the surface.
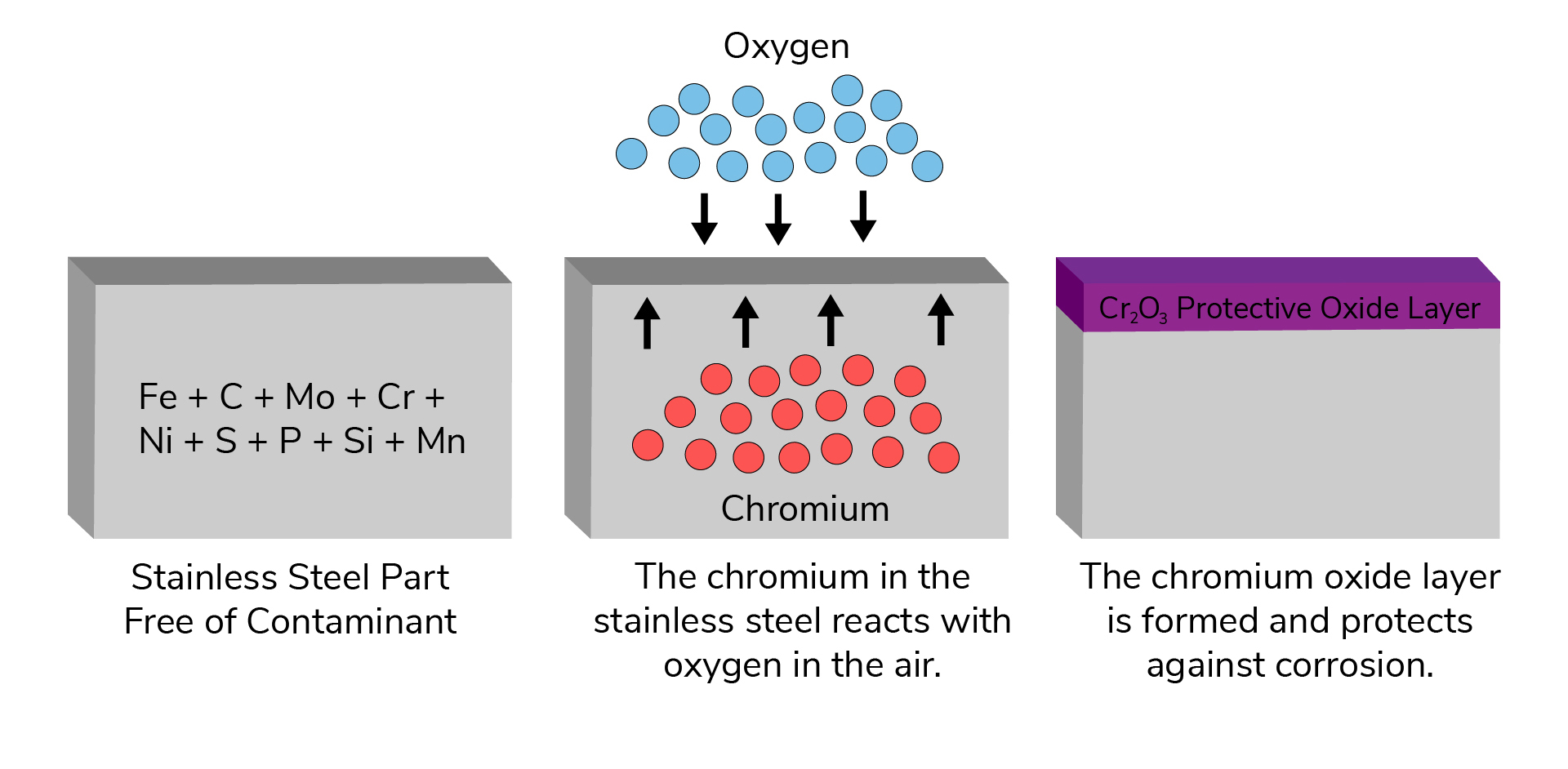
How the Passivation Process Restores the Chromium Oxide Layer of Stainless Steel
The passivation process restores the chromium oxide layer on stainless steel by removing contaminants and enhancing the natural formation of the protective layer.
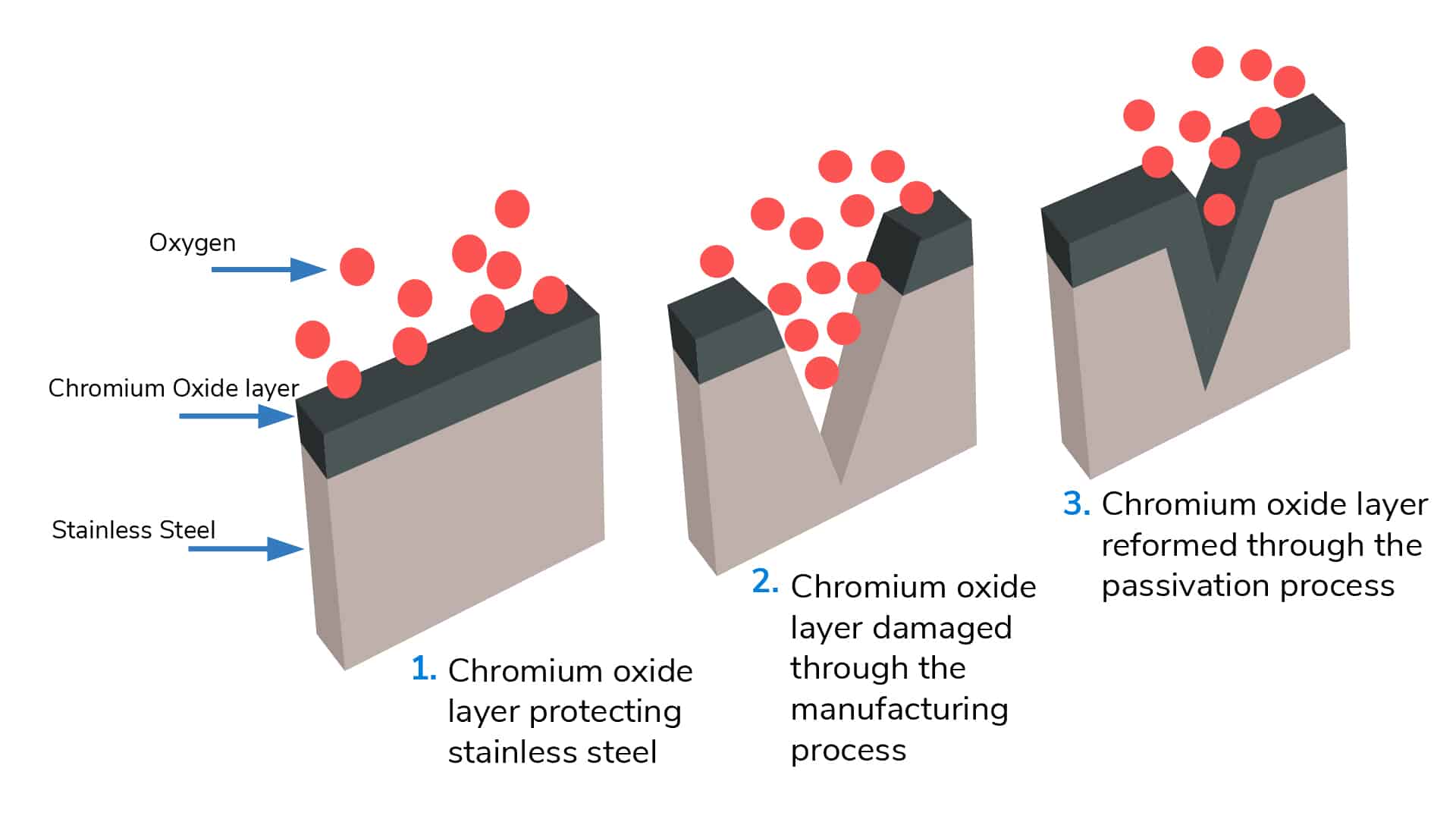
Pickling vs. Passivation
While often confused, pickling is a more aggressive chemical process used to remove heavy scale and oxides from the surface. Unlike passivation, it does not promote the formation of a passive film.
What is Electropolishing?
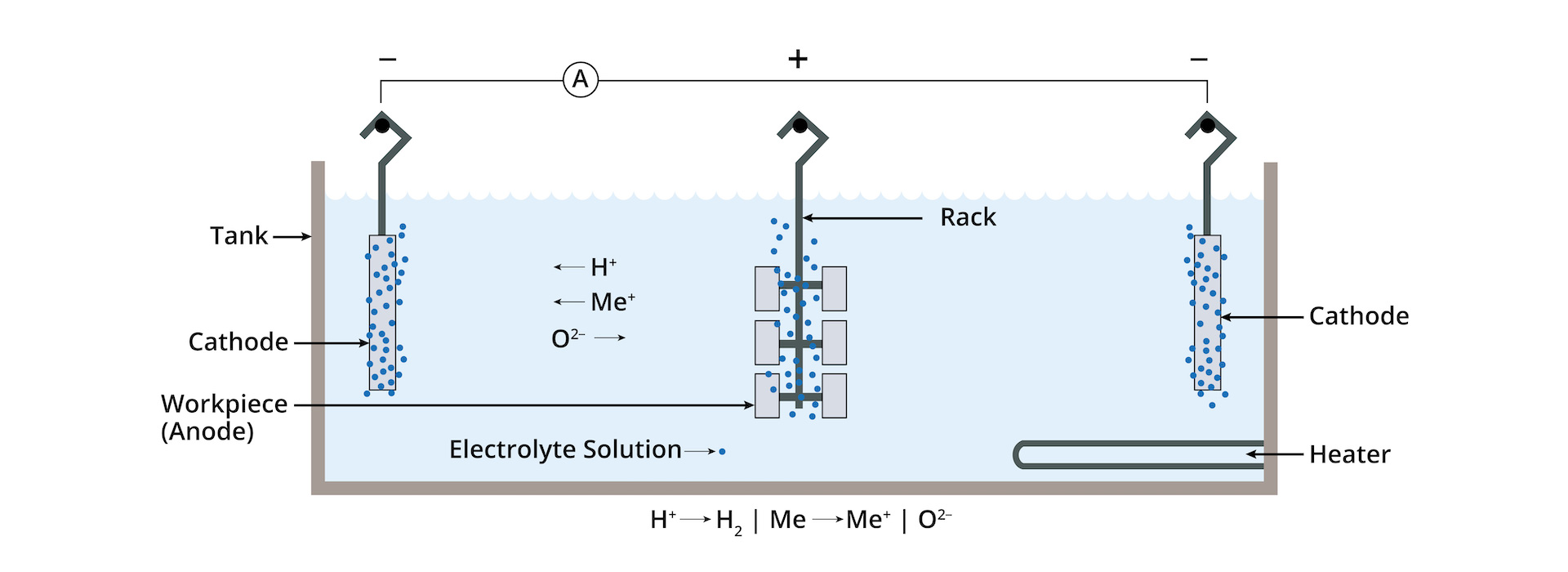
Electropolishing stands as an electrochemical technique known for its prowess in refining metal surfaces. Unlike electroplating, which adds metal layers, electropolishing delicately removes the outer layer of a metal component, akin to peeling off its ‘skin.’ This meticulous process is adept at addressing microscopic imperfections within the finish, offering thorough cleaning, deburring, and passivation. It’s a staple in manufacturing, ensuring parts emerge with pristine surfaces and enhanced durability.
Electropolishing Tank Diagram
Why Passivation Matters
Even high-grade stainless steel can be compromised by manufacturing processes like machining, grinding, or welding. These operations can leave behind microscopic iron particles or disturb the natural oxide film, making the material vulnerable to corrosion.
Passivation restores and enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel, ensuring it performs as expected in harsh or critical environments.
At New England Electropolishing, we understand the importance of the passivation of stainless steel. Our team of experts employs state-of-the-art techniques and industry-leading practices to execute precise and effective stainless steel passivation processes.
At New England Electropolishing, passivation is one of the ways we help manufacturers across industries—from medical to aerospace to food processing—ensure their parts meet strict performance and durability standards.
Beyond traditional passivation methods, our electrochemical passivation techniques provide unparalleled results. Stainless steel passivation not only removes impurities but also optimizes the surface, resulting in a smoother, more uniform finish. This advanced approach ensures maximum corrosion resistance and longevity for your stainless steel components.
Improve Your Stainless Steel Parts and Componants with New England Electropolishing
Whether for medical equipment, aerospace components, food processing machinery, load cells, or architectural features, passivation plays a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity and performance of stainless steel. At New England Electropolishing, we’re committed to delivering superior results, elevating the durability of your stainless steel products through our expert passivation techniques.
Experience the difference passivation can make in preserving and enhancing your stainless steel investments. Contact New England Electropolishing today to learn more about our passivation services and unlock the full potential of stainless steel in your applications.
What's the Difference Between Electropolishing & Passivation
Electropolishing Resources

What is Electropolishing?
Electropolishing is an electrochemical and reverse plating process that removes the outer layer of skin on a metal...
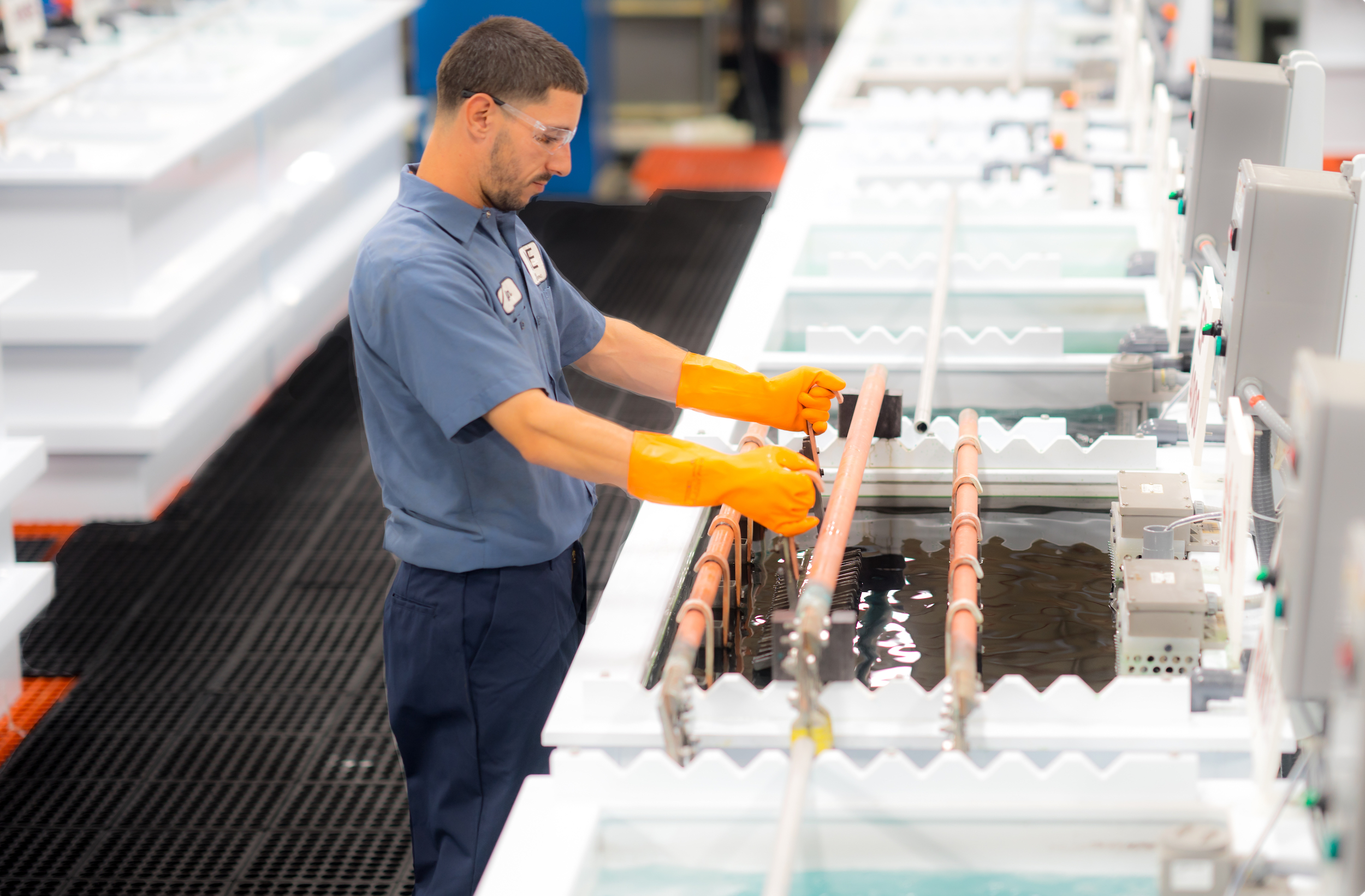

The Electropolishing Process
The electropolishing process is initiated by immersing a metal part into a temperature-controlled bath of electrolyte...

Benefits of Electropolishing
Curious about the benefits of putting your parts through the electropolishing process? Read along below where we...

How Much Material Does Electropolishing Remove?
Electropolishing, when done properly is a highly controllable process which removes as little as...

How Much Will Electropolishing Improve the Surface Finish of My Part?
Ra and RMS are both representations of surface roughness. Ra is calculated as the roughness average of a surface’s...

Electropolishing Frequently Asked Questions
Learn the difference between electropolishing and electroplating as well as how the electropolishing process works...

What is ASTM B912?
ASTM B912 is an industry standard for the passivation of stainless steel alloys through electropolishing...

What is ASTM A967?
ASTM A967 is an industry standard specification for the chemical passivation treatments for stainless...

What is ISO 13485?
ISO 13485 is a standard that applies specifically to medical devices. ISO 13485 is designed to be...
