Understanding 410 Grade Stainless Steel
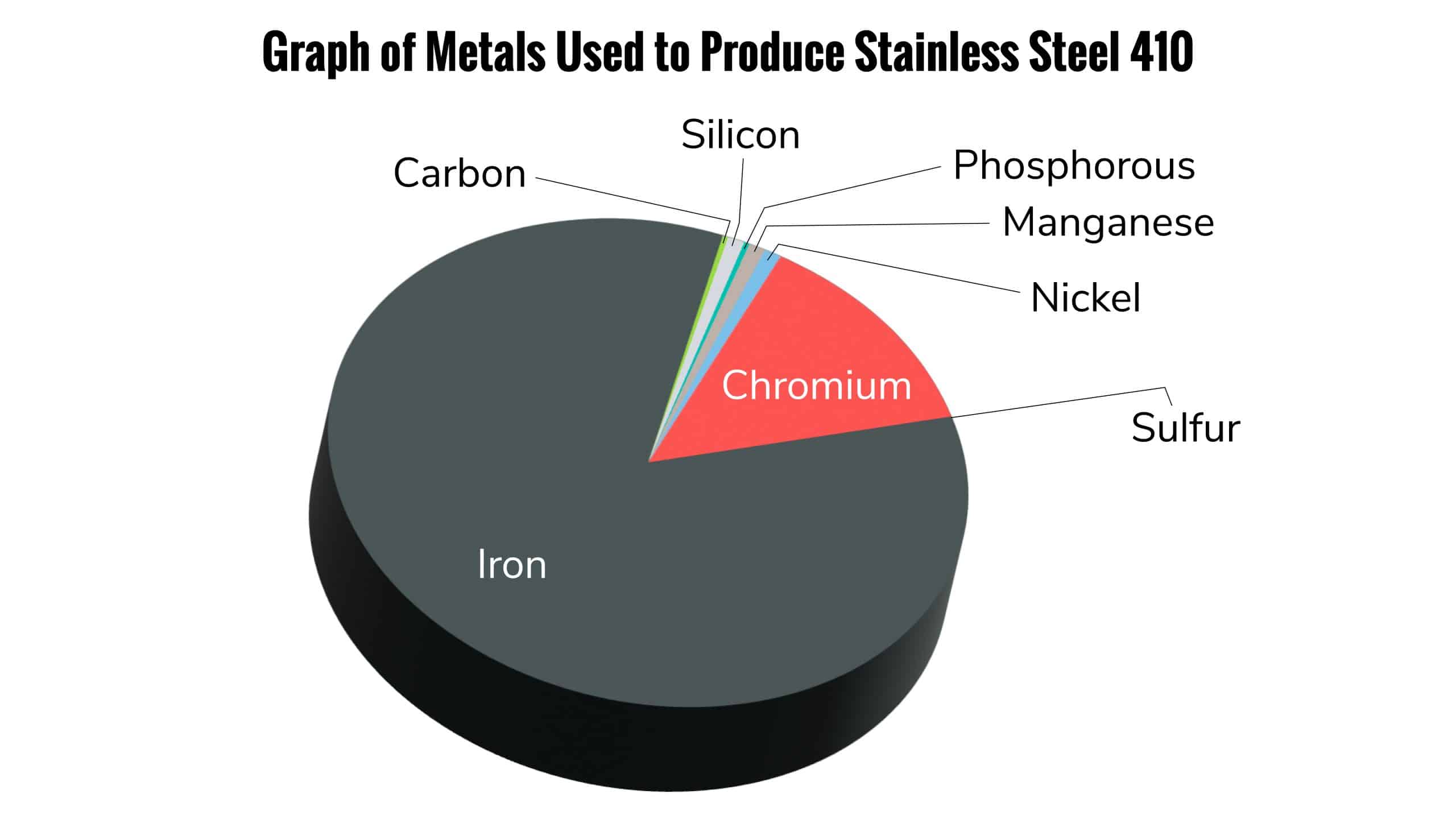
Grade 410 stainless steel is a martensitic alloy known for its high strength and moderate corrosion resistance. Composed primarily of iron, chromium, and carbon, this steel grade is often used in applications where strength and durability are essential, such as in cutlery, fasteners, and machine parts.

History of 410 Stainless Steel
410 stainless steel was developed in the early 20th century as a solution for industries that needed a material combining the advantages of carbon steel’s strength with the corrosion resistance of chromium. Martensitic stainless steels like 410 emerged as a versatile solution for applications that required heat treatment for enhanced hardness and durability.
Advantages of 410 Stainless Steel
- High Strength and Hardness: After heat treatment, 410 stainless steel can achieve high levels of hardness, making it ideal for applications requiring wear resistance.
- Moderate Corrosion Resistance: While not as corrosion-resistant as austenitic grades like 304 or 316, 410 provides adequate protection in mild environments.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to higher grades of stainless steel, 410 is relatively affordable, making it attractive for cost-conscious projects.
Disadvantages of 410 Stainless Steel
- Limited Corrosion Resistance: 410 stainless steel may rust or corrode in more aggressive or salty environments, requiring maintenance or coating for additional protection.
- Brittleness After Heat Treatment: The high hardness achieved through heat treatment can also make 410 stainless steel more brittle, limiting its use in applications requiring ductility.
Common Applications of 410 Stainless Steel
Grade 410 stainless steel is widely used in industries requiring high strength and moderate corrosion resistance. Key applications include:
- Cutlery and Kitchenware: Commonly used for knives and utensils due to its balance of strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
- Fasteners and Bolts: Its strength makes it ideal for screws, bolts, and other fasteners used in mild environments.
- Pump Shafts and Valves: Its wear resistance makes it useful in components that must withstand mechanical stress and moderate corrosion.
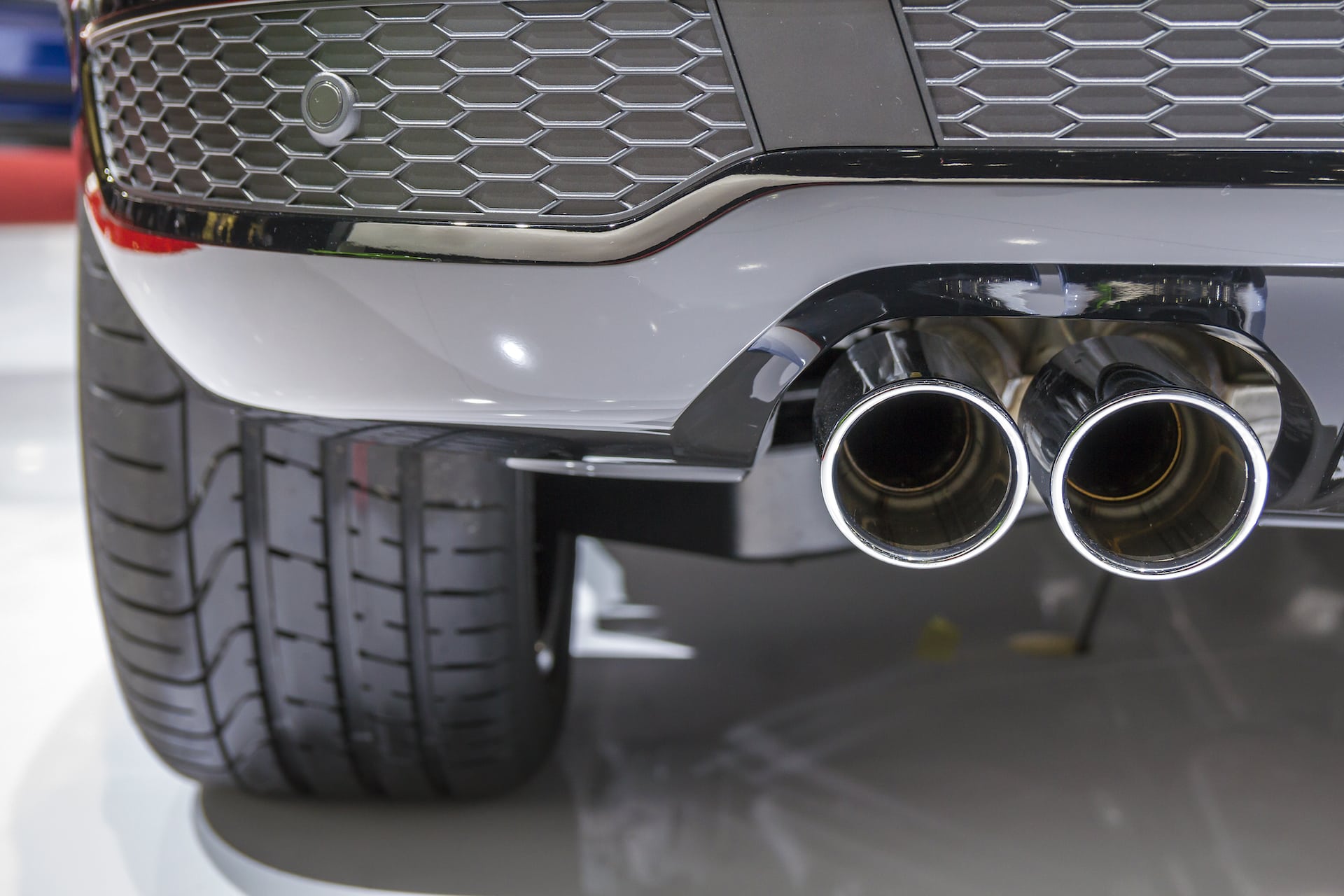
- Automotive Parts: Frequently used in parts like exhaust systems and manifolds that experience heat and moderate corrosive exposure.
- Petrochemical and Refining Equipment: Suitable for environments where a combination of heat resistance and moderate corrosion protection is required.










