Understanding 304 Grade Stainless Steel
304 grade stainless steel is one of the most widely used and versatile stainless steels on the market. Known for its excellent corrosion resistance and durability, 304 grade is often used for both domestic and industrial applications. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at the history, properties, and common uses of this stainless steel grade, along with its advantages and disadvantages.

What is 304 Grade Stainless Steel?
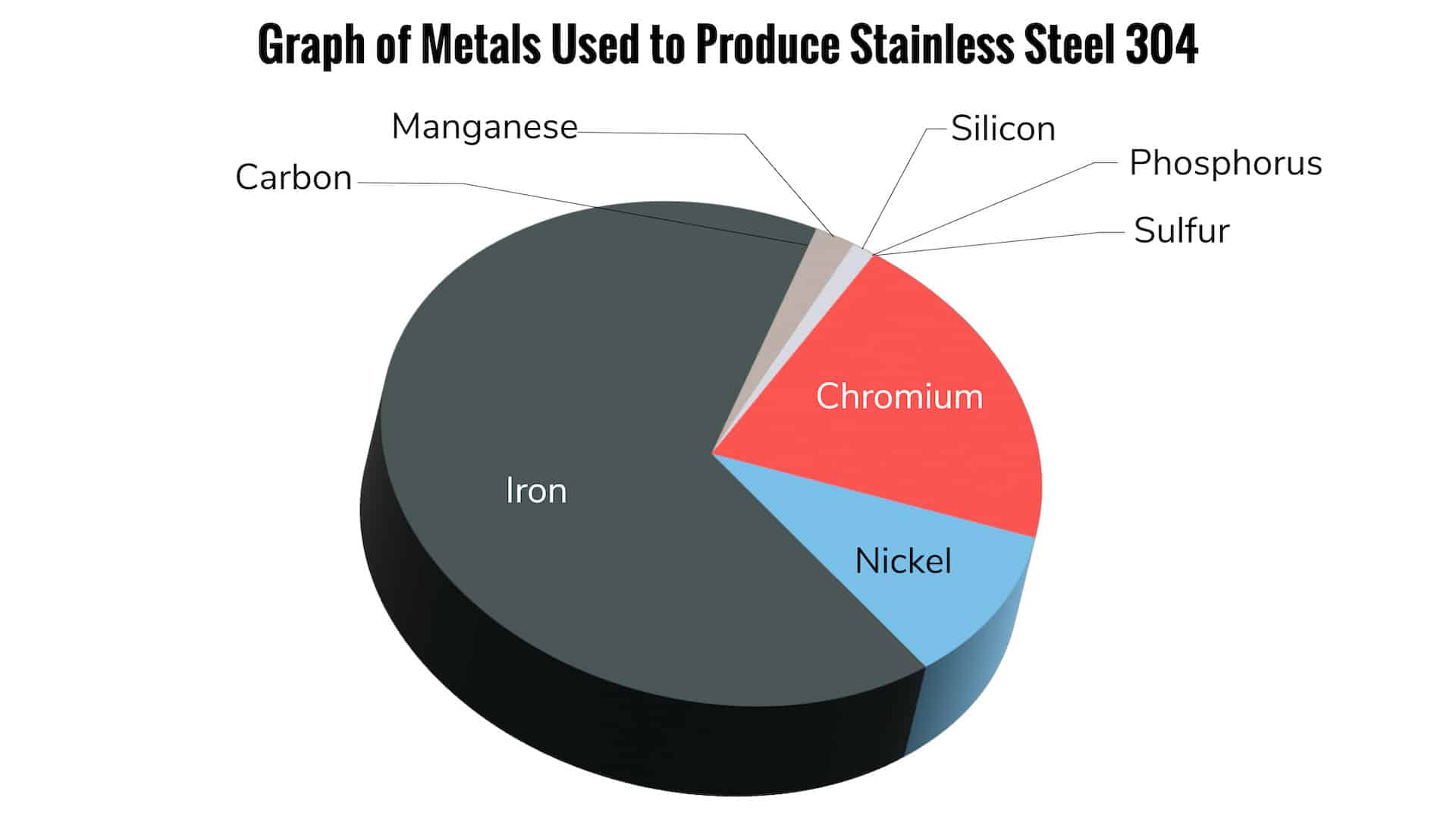
304 stainless steel is part of the austenitic family, which is characterized by high levels of chromium and nickel, typically containing 18-20% chromium and 8-10.5% nickel. It is often referred to as “18/8 stainless steel” due to this composition. This blend gives it excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation, while also maintaining good formability and weldability.
History of 304 Stainless Steel
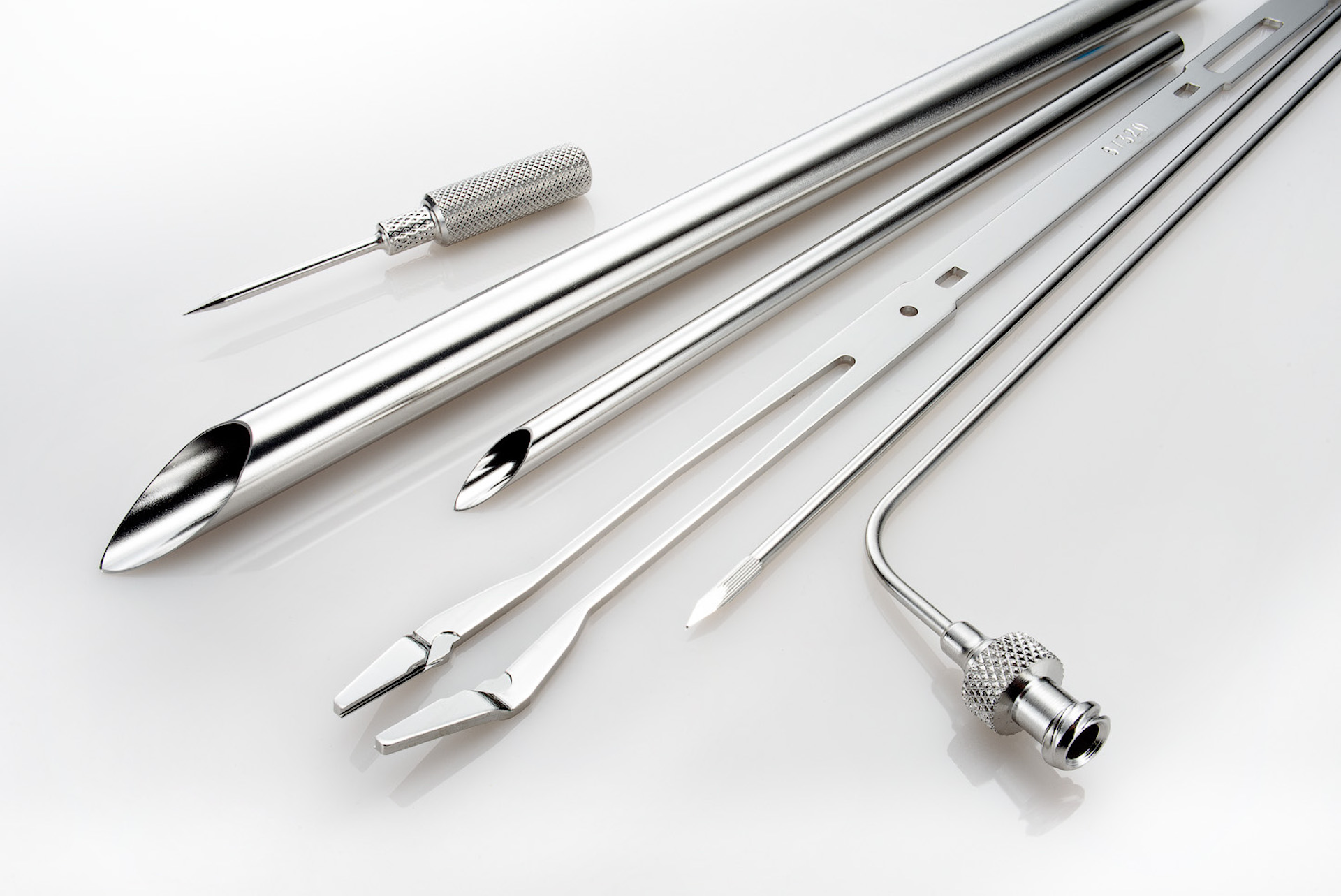
The development of stainless steel dates back to the early 20th century, when metallurgists discovered the benefits of adding chromium to steel to improve its corrosion resistance. 304 grade stainless steel was refined during this period and quickly gained popularity in industries like food processing, manufacturing, medical device manufacturing and architecture due to its durability and resistance to corrosion, rust and staining.
Advantages of 304 Grade Stainless Steel
- Corrosion Resistance: One of the most important benefits of 304 stainless steel is its high corrosion resistance. It can withstand exposure to moisture, acidic substances, and even saltwater, making it ideal for various environments.
- Durability: 304 grade is known for its strength and toughness, which allows it to handle high-stress applications without cracking or deforming.
- Ease of Fabrication: This grade of stainless steel is highly workable. It can be easily formed, welded, and cut, making it a popular choice for both large-scale industrial projects and smaller domestic uses.
- Hygienic Properties: Thanks to its smooth surface, 304 stainless steel is easy to clean and maintain, making it a favorite in industries like food and beverage, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals.
- Aesthetic Appeal: 304 stainless steel has a shiny, attractive finish that makes it a popular material for kitchenware and architectural features.
Disadvantages of 304 Grade Stainless Steel
- Cost: While 304 grade offers many benefits, it can be more expensive than other materials due to the high cost of chromium and nickel.
- Susceptibility to Chlorides: Although it has good general corrosion resistance, 304 stainless steel is less resistant to chlorides, such as salt, which can cause pitting or corrosion in some environments (for example, marine applications).
- Magnetism: 304 stainless steel is typically non-magnetic, but it can become slightly magnetic after cold working, which might be a disadvantage in some applications requiring completely non-magnetic properties.
Common Applications of 304 Grade Stainless Steel
Due to its versatility, 304 grade stainless steel is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Its excellent corrosion resistance and ease of cleaning make 304 stainless steel the top choice for equipment like sinks, food preparation tables, brewing equipment, and dairy equipment.
- Kitchenware and Appliances: Many everyday items, including pots, pans, and kitchen appliances, are made from 304 stainless steel due to its resistance to staining and rust.
- Architectural Applications: Handrails, countertops, and decorative panels are often made from 304 stainless steel, especially in high-traffic areas where durability and aesthetics are key.
- Medical Equipment: Its hygienic properties make 304 stainless steel a go-to material for surgical instruments, hospital trays, and other sterile environments.
- Chemical and Petroleum Industries: 304 stainless steel is often used in tanks, pipes, and heat exchangers that are exposed to corrosive materials.
- Automotive and Aerospace: Its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion also make it useful in parts exposed to harsh environments such as automotive and aerospace environments.
Conclusion
304 grade stainless steel is a highly durable, corrosion-resistant material that has become an essential part of many industries, from food processing to medical device manufacturing. Its ease of fabrication, strength, and aesthetic qualities make it a versatile choice, although it can be pricier than other materials and isn’t the best option for highly chloride-rich environments.
With its wide range of applications, 304 stainless steel is often the first choice for projects that require a reliable, easy-to-maintain material that can withstand tough conditions while looking sleek and modern.







